|
|
|
|
@ -1,219 +1,221 @@
|
|
|
|
|
# CmBacktrace: ARM Cortex-M 系列 MCU 错误追踪库
|
|
|
|
|
# CmBacktrace: ARM Cortex-M series MCU error tracking library
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[中文页](README_ZH.md) | English
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/releases/latest) [](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/compare/1.0.0...master) [](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/armink/CmBacktrace/master/LICENSE)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
## 0、CmBacktrace 是什么
|
|
|
|
|
## 0、What is CmBacktrace
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[CmBacktrace](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace) (Cortex Microcontroller Backtrace)是一款针对 ARM Cortex-M 系列 MCU 的错误代码自动追踪、定位,错误原因自动分析的开源库。主要特性如下:
|
|
|
|
|
[CmBacktrace](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace) (Cortex Microcontroller Backtrace) is an open source library that automatically tracks and locates error codes for ARM Cortex-M series MCUs, and automatically analyzes the causes of errors. The main features are as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 支持的错误包括:
|
|
|
|
|
- 断言(assert)
|
|
|
|
|
- 故障(Hard Fault, Memory Management Fault, Bus Fault, Usage Fault, Debug Fault)
|
|
|
|
|
- 故障原因 **自动诊断** :可在故障发生时,自动分析出故障的原因,定位发生故障的代码位置,而无需再手动分析繁杂的故障寄存器;
|
|
|
|
|
- 输出错误现场的 **函数调用栈**(需配合 addr2line 工具进行精确定位),还原发生错误时的现场信息,定位问题代码位置、逻辑更加快捷、精准。也可以在正常状态下使用该库,获取当前的函数调用栈;
|
|
|
|
|
- 支持 裸机 及以下操作系统平台:
|
|
|
|
|
- Supported errors include:
|
|
|
|
|
- Assert
|
|
|
|
|
- Fault (Hard Fault, Memory Management Fault, Bus Fault, Usage Fault, Debug Fault)
|
|
|
|
|
- Failure reason **Automatic diagnosis**: When a failure occurs, the cause of the failure can be automatically analyzed, and the code location of the failure can be located, without the need to manually analyze the complicated fault registers;
|
|
|
|
|
-Output the **function call stack** of the error site (need to cooperate with the addr2line tool for precise positioning), restore the field information when the error occurred, and locate the problem code location and logic more quickly and accurately. You can also use the library under normal conditions to get the current function call stack;
|
|
|
|
|
- Support bare metal and the following operating system platforms:
|
|
|
|
|
- [RT-Thread](http://www.rt-thread.org/)
|
|
|
|
|
- UCOS
|
|
|
|
|
- FreeRTOS(需修改源码)
|
|
|
|
|
- 根据错误现场状态,输出对应的 线程栈 或 C 主栈;
|
|
|
|
|
- 故障诊断信息支持多国语言(目前:简体中文、英文);
|
|
|
|
|
- 适配 Cortex-M0/M3/M4/M7 MCU;
|
|
|
|
|
- 支持 IAR、KEIL、GCC 编译器;
|
|
|
|
|
- FreeRTOS (source code needs to be modified)
|
|
|
|
|
- According to the error scene status, output the corresponding thread stack or C main stack;
|
|
|
|
|
- The fault diagnosis information supports multiple languages (currently: Simplified Chinese, English);
|
|
|
|
|
- Adapt to Cortex-M0/M3/M4/M7 MCU;
|
|
|
|
|
- Support IAR, KEIL, GCC compiler;
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
## 1、为什么选择 CmBacktrace
|
|
|
|
|
## 1. Why choose CmBacktrace
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
**入门新人** :对于从 C51 、MSP430 等简单单片机转而使用更加复杂的 ARM 新人来说,时不时出现的 "hard falut" 死机会让新人瞬间懵掉。定位错误的方法也往往是连接上仿真器,一步步 F10/F11 单步,定位到具体的错误代码,再去猜测、排除、推敲错误原因,这种过程十分痛苦。
|
|
|
|
|
**Beginner Newcomer**: For newcomers who switch from simple microcontrollers such as C51 and MSP430 to more complex ARM, the chance of "hard falut" death from time to time makes newcomers instantly stunned. The method of locating errors is often to connect to the emulator, step by step F10/F11, locate the specific error code, and then guess, eliminate, and deliberate on the cause of the error. This process is very painful.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
**熟练老手** :慢慢的大家知道可以通过故障寄存器信息来定位故障原因及故障代码地址,虽然这样能解决一小部分问题,但是重复的、繁琐的分析过程也会耽误很多时间。而且对于一些复杂问题,只依靠代码地址是无法解决的,必须得还原错误现场的函数调用逻辑关系。虽然连接仿真器可以查看到的函数调用栈,但故障状态下是无法显示的,所以还是得一步步 F10/F11 单步去定位错误代码的位置。另外,还有两种场景,
|
|
|
|
|
**Skilled veteran**: Slowly everyone knows that the fault cause and fault code address can be located through the fault register information. Although this can solve a small part of the problem, the repeated and tedious analysis process will also delay a lot of time. Moreover, for some complex problems, it is impossible to solve only by the code address, and the function call logic relationship of the wrong scene must be restored. Although the function call stack can be viewed by connecting to the emulator, it cannot be displayed in the fault state, so it is necessary to step by step F10/F11 to locate the error code. In addition, there are two scenarios,
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 1、很多产品真机调试时必须断开仿真器
|
|
|
|
|
- 2、问题确实存在,但是极难被重现
|
|
|
|
|
1. The emulator must be disconnected when debugging many products
|
|
|
|
|
2. The problem does exist, but it is extremely difficult to reproduce
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
所以定位这类问题就显得难上加难。
|
|
|
|
|
So locating such problems is even more difficult.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
**使用本库** :上述所有问题都迎刃而解,可以将错误信息输出到控制台上,还可以将错误信息使用 [EasyFlash](https://github.com/armink/EasyFlash) 的 Log 功能保存至 Flash 中,设备死机后重启依然能够读取上次的错误信息。CmBacktrace 输出的信息包括函数调用栈、故障诊断结果、堆栈、故障寄存器及产品固件信息,极大的提升了错误定位的效率及准确性。
|
|
|
|
|
**Use this library**: All the above problems can be solved easily. The error message can be output to the console, and the error message can also be saved using the Log function of [EasyFlash](https://github.com/armink/EasyFlash) In Flash, the last error message can still be read after the device crashes and restarts. The information output by CmBacktrace includes function call stack, fault diagnosis result, stack, fault register and product firmware information, which greatly improves the efficiency and accuracy of error location.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
俗话说,工欲善其事,必先利其器。所以有时候做事效率低的原因也许是,你会用的工具种类太少。
|
|
|
|
|
As the saying goes, a worker must first sharpen his tools if he wants to do his job well. So sometimes the reason for the low efficiency may be that you will use too few types of tools.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
**合作、贡献** :开源软件的发展离不开大家的支持,欢迎大家多提建议,也希望更多的人一起参与进来,共同提高 。如果觉得这个开源项目很赞,可以点击 [项目主页](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace) **([Github](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace)|[OSChina](http://git.oschina.net/armink/CmBacktrace)|[Coding](https://coding.net/u/armink/p/CmBacktrace/git))** 右上角的 **Star** ,同时把它推荐给更多有需要的朋友。
|
|
|
|
|
**Cooperation, Contribution**: The development of open source software is inseparable from everyone's support. You are welcome to make more suggestions and hope that more people will join in and improve together. If you think this open source project is great, you can click [Project Homepage](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace) **([Github](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace)|[OSChina](http://git.oschina.net/armink/CmBacktrace)|[Coding](https://coding.net/u/armink/p/CmBacktrace/git))** Star** in the upper right corner, At the same time recommend it to more friends in need.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
## 2、CmBacktrace 如何使用
|
|
|
|
|
## 2. How to use CmBacktrace
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 2.1 演示
|
|
|
|
|
### 2.1 Demo
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
该演示分如下几个步骤:
|
|
|
|
|
The demonstration is divided into the following steps:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
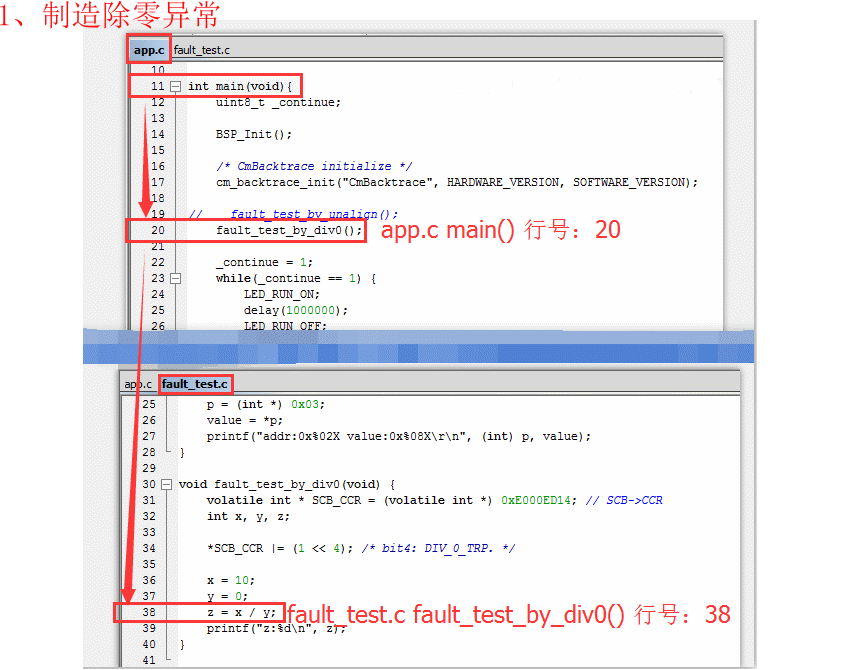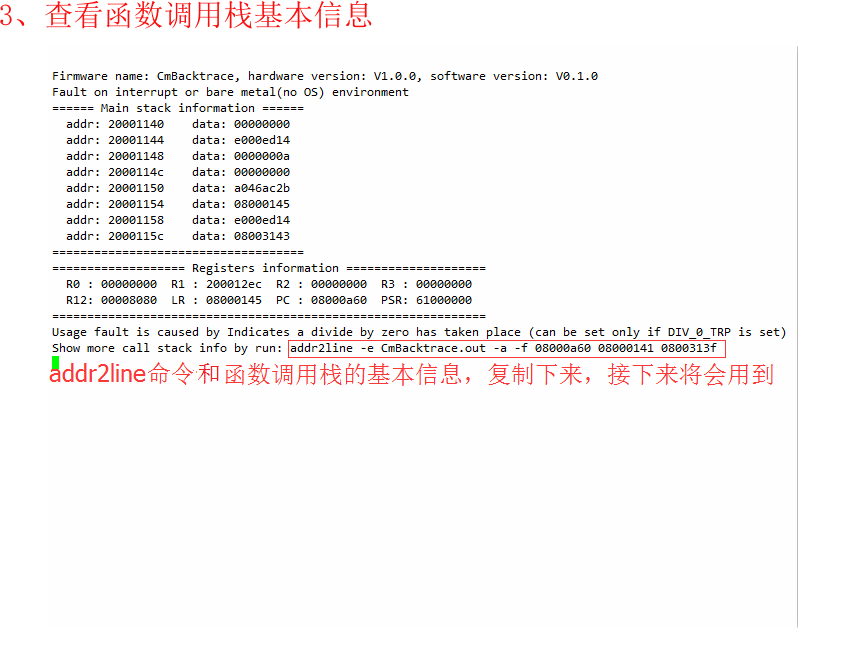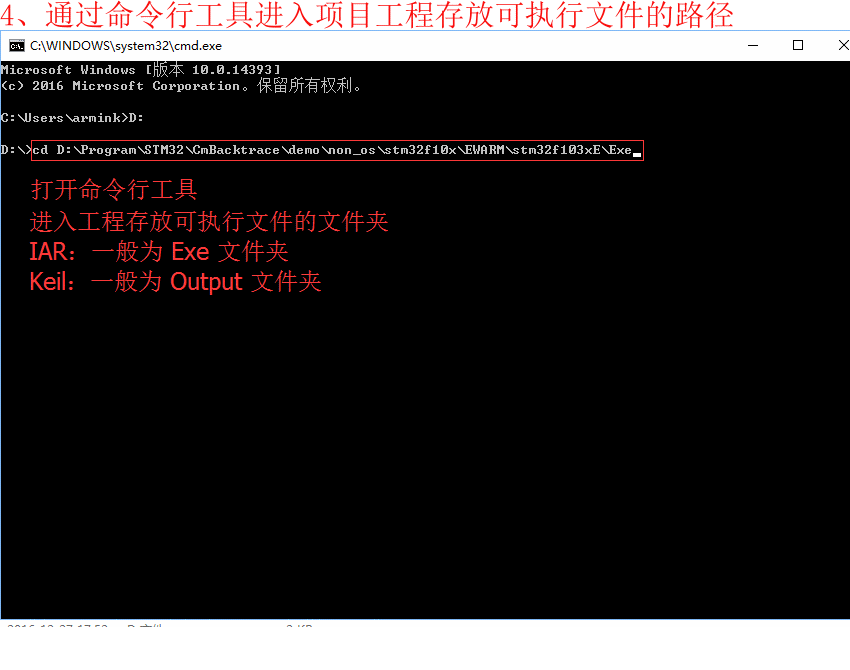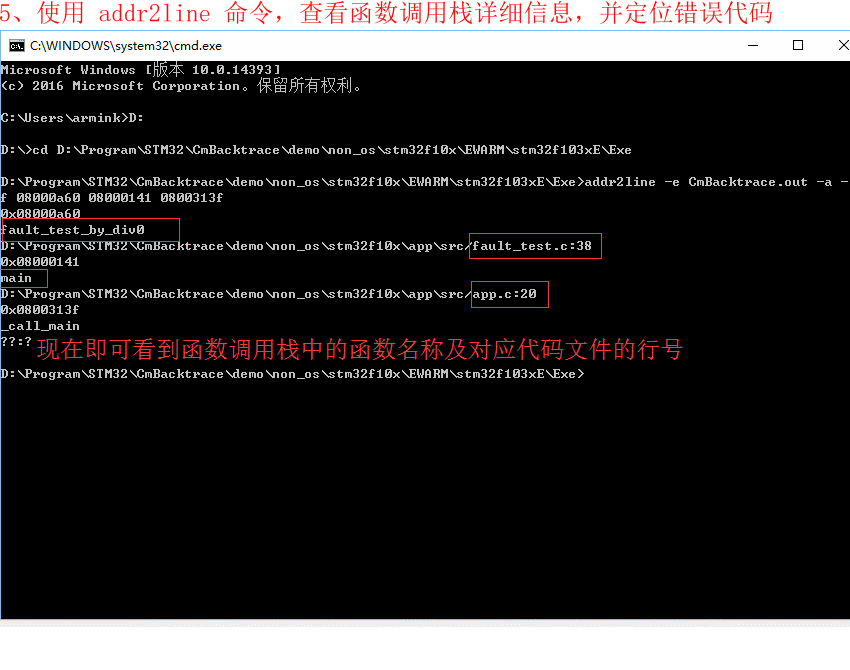
- 1、制造除零异常([IAR 工程,点击查看源码](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/tree/master/demos/non_os/stm32f10x/app/src))
|
|
|
|
|
- 2、查看错误诊断信息
|
|
|
|
|
- 3、查看函数调用栈基本信息
|
|
|
|
|
- 4、通过命令行工具进入项目工程存放可执行文件的路径
|
|
|
|
|
- 5、使用 addr2line 命令,查看函数调用栈详细信息,并定位错误代码
|
|
|
|
|
1. Manufacturing division by zero exception ([IAR project, click to view source code](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/tree/master/demos/non_os/stm32f10x/app/src))
|
|
|
|
|
2. View error diagnosis information
|
|
|
|
|
3. View the basic information of the function call stack
|
|
|
|
|
4. Enter the path where the executable file is stored in the project project through the command line tool
|
|
|
|
|
5. Use the addr2line command to view the function call stack details and locate the error code
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 2.2 Demo
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|目录|平台|链接|
|
|
|
|
|
|Catalog|Platform|Link|
|
|
|
|
|
|:--|:--:|:--:|
|
|
|
|
|
| `\demos\non_os\stm32f10x` |裸机 STM32 Cortex-M3|[点击查看](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/tree/master/demos/non_os/stm32f10x)|
|
|
|
|
|
| `\demos\os\rtthread\stm32f4xx`|RT-Thread STM32 Cortex-M4|[点击查看](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/tree/master/demos/os/rtthread/stm32f4xx)|
|
|
|
|
|
| `\demos\os\ucosii\stm32f10x` |UCOSII STM32 Cortex-M3|[点击查看](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/tree/master/demos/os/ucosii/stm32f10x)|
|
|
|
|
|
| `\demos\os\freertos\stm32f10x` |FreeRTOS STM32 Cortex-M3|[点击查看](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/tree/master/demos/os/freertos/stm32f10x)|
|
|
|
|
|
| `\demos\non_os\stm32f10x` |bare metal STM32 Cortex-M3|[click to view](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/tree/master/demos/non_os/stm32f10x)|
|
|
|
|
|
| `\demos\os\rtthread\stm32f4xx`|RT-Thread STM32 Cortex-M4|[Click to view](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/tree/master/demos/os/rtthread/stm32f4xx)|
|
|
|
|
|
| `\demos\os\ucosii\stm32f10x` |UCOSII STM32 Cortex-M3|[Click to view](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/tree/master/demos/os/ucosii/stm32f10x)|
|
|
|
|
|
| `\demos\os\freertos\stm32f10x` |FreeRTOS STM32 Cortex-M3|[Click to view](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/tree/master/demos/os/freertos/stm32f10x)|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 2.3 移植说明
|
|
|
|
|
### 2.3 Porting instructions
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.3.1 准备工作
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.3.1 Preparation
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 1、查看 `\demos` 目录下有没有合适自己的 Demo ,如有类似,则建议在其基础上修改
|
|
|
|
|
- 2、明确操作系统/裸机平台及 CPU 平台
|
|
|
|
|
- 3、将 `\src` 下的全部源文件添加至产品工程中,并保证源码目录被添加至头文件路径
|
|
|
|
|
- 4、cmb_fault.s 汇编文件([点击查看](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/tree/master/cm_backtrace/fault_handler))可以选择性添加至工程,添加后需要把项目原有的 `HardFault_Handler` 注释掉
|
|
|
|
|
- 5、把 `cm_backtrace_init` 函数放在项目初始化地方执行
|
|
|
|
|
- 6、将 `cm_backtrace_assert` 放在项目的断言函数中执行,具体使用方法参照下面的 API 说明
|
|
|
|
|
- 7、如果第 4 步骤没有将 cmb_fault.s 汇编文件启用,则需要将 `cm_backtrace_fault` 放到故障处理函数(例如: `HardFault_Handler` )中执行,具体使用方法参照下面的 API 说明
|
|
|
|
|
1. Check whether there is a suitable Demo in the `\demos` directory, if there is a similar, it is recommended to modify it on the basis of it
|
|
|
|
|
2. Identify the operating system/bare metal platform and CPU platform
|
|
|
|
|
3. Add all source files under `\src` to the product project, and ensure that the source code directory is added to the header file path
|
|
|
|
|
4. The cmb_fault.s assembly file ([click to view](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/tree/master/cm_backtrace/fault_handler)) can be optionally added to the project. After adding, you need to add the original project `HardFault_Handler` comment out
|
|
|
|
|
5. Put the `cm_backtrace_init` function in the project initialization place for execution
|
|
|
|
|
6. Put `cm_backtrace_assert` in the assertion function of the project for execution. For specific usage, please refer to the API description below
|
|
|
|
|
7. If the cmb_fault.s assembly file is not enabled in step 4, you need to put `cm_backtrace_fault` in the fault handling function (for example: `HardFault_Handler`) for execution. For details, refer to the API description below
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.3.2 配置说明
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.3.2 Configuration Instructions
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
配置文件名: `cmb_cfg.h` ,针对不同的平台和场景,用户需要自自行手动配置,常用配置如下:
|
|
|
|
|
Configuration file name: `cmb_cfg.h`, users need to manually configure themselves for different platforms and scenarios. Common configurations are as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 配置名称 |功能|备注|
|
|
|
|
|
| Configuration name | Function | Remarks |
|
|
|
|
|
|:--|:--|:--|
|
|
|
|
|
|cmb_println(...)|错误及诊断信息输出|必须配置|
|
|
|
|
|
|CMB_USING_BARE_METAL_PLATFORM|是否使用在裸机平台|使用则定义该宏|
|
|
|
|
|
|CMB_USING_OS_PLATFORM|是否使用在操作系统平台|操作系统与裸机必须二选一|
|
|
|
|
|
|CMB_OS_PLATFORM_TYPE|操作系统平台|RTT/UCOSII/UCOSIII/FREERTOS|
|
|
|
|
|
|CMB_CPU_PLATFORM_TYPE|CPU平台|M0/M3/M4/M7|
|
|
|
|
|
|CMB_USING_DUMP_STACK_INFO|是否使用 Dump 堆栈的功能|使用则定义该宏|
|
|
|
|
|
|CMB_PRINT_LANGUAGE|输出信息时的语言|CHINESE/ENGLISH|
|
|
|
|
|
|cmb_println(...)|Error and diagnostic information output|Must be configured|
|
|
|
|
|
|CMB_USING_BARE_METAL_PLATFORM|Whether it is used on a bare metal platform|Define this macro if it is used|
|
|
|
|
|
|CMB_USING_OS_PLATFORM|Whether it is used on the operating system platform|Operating system and bare metal must choose one of two|
|
|
|
|
|
|CMB_OS_PLATFORM_TYPE|Operating System Platform|RTT/UCOSII/UCOSIII/FREERTOS|
|
|
|
|
|
|CMB_CPU_PLATFORM_TYPE|CPU platform|M0/M3/M4/M7|
|
|
|
|
|
|CMB_USING_DUMP_STACK_INFO|Whether to use Dump stack function|Use to define this macro|
|
|
|
|
|
|CMB_PRINT_LANGUAGE|Language when outputting information|CHINESE/ENGLISH|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
> 注意:以上部分配置的内容可以在 `cmb_def.h` 中选择,更多灵活的配置请阅读源码
|
|
|
|
|
> Note: The content of the above configuration can be selected in `cmb_def.h`, please read the source code for more flexible configuration
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 2.4 API 说明
|
|
|
|
|
### 2.4 API description
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.4.1 库初始化
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.4.1 Library initialization
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```C
|
|
|
|
|
void cm_backtrace_init(const char *firmware_name, const char *hardware_ver, const char *software_ver)
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|参数 |描述|
|
|
|
|
|
|:----- |:----|
|
|
|
|
|
|firmware_name |固件名称,需与编译器生成的固件名称对应|
|
|
|
|
|
|hardware_ver |固件对应的硬件版本号|
|
|
|
|
|
|software_ver |固件的软件版本号|
|
|
|
|
|
|Parameter |Description|
|
|
|
|
|
|:----- |:----|
|
|
|
|
|
|firmware_name |firmware name, which must correspond to the firmware name generated by the compiler|
|
|
|
|
|
|hardware_ver |The hardware version number corresponding to the firmware|
|
|
|
|
|
|software_ver |Software version number of the firmware|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
> **注意** :以上入参将会在断言或故障时输出,主要起了追溯的作用
|
|
|
|
|
> **Note**: The above input parameters will be output in case of assertion or failure, mainly for retrospective purposes
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.4.2 获取函数调用栈
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.4.2 Get function call stack
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```C
|
|
|
|
|
size_t cm_backtrace_call_stack(uint32_t *buffer, size_t size, uint32_t sp)
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|参数 |描述|
|
|
|
|
|
|:----- |:----|
|
|
|
|
|
|buffer |存储函数调用栈的缓冲区|
|
|
|
|
|
|size |缓冲区大小|
|
|
|
|
|
|sp |待获取的堆栈指针|
|
|
|
|
|
|Parameter |Description|
|
|
|
|
|
|:----- |:----|
|
|
|
|
|
|buffer |Buffer for storing function call stack|
|
|
|
|
|
|size |Buffer size|
|
|
|
|
|
|sp |Stack pointer to be obtained|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
示例:
|
|
|
|
|
Example:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```C
|
|
|
|
|
/* 建立深度为 16 的函数调用栈缓冲区,深度大小不应该超过 CMB_CALL_STACK_MAX_DEPTH(默认16) */
|
|
|
|
|
/* Create a function call stack buffer with a depth of 16, and the depth should not exceed CMB_CALL_STACK_MAX_DEPTH (default 16) */
|
|
|
|
|
uint32_t call_stack[16] = {0};
|
|
|
|
|
size_t i, depth = 0;
|
|
|
|
|
/* 获取当前环境下的函数调用栈,每个元素将会以 32 位地址形式存储, depth 为函数调用栈实际深度 */
|
|
|
|
|
/* Get the function call stack in the current environment, each element will be stored as a 32-bit address, and depth is the actual depth of the function call stack */
|
|
|
|
|
depth = cm_backtrace_call_stack(call_stack, sizeof(call_stack), cmb_get_sp());
|
|
|
|
|
/* 输出当前函数调用栈信息
|
|
|
|
|
* 注意:查看函数名称及具体行号时,需要使用 addr2line 工具转换
|
|
|
|
|
/* Output current function call stack information
|
|
|
|
|
* Note: When viewing the function name and specific line number, you need to use the addr2line tool to convert
|
|
|
|
|
*/
|
|
|
|
|
for (i = 0; i < depth; i++) {
|
|
|
|
|
for (i = 0; i <depth; i++) {
|
|
|
|
|
printf("%08x ", call_stack[i]);
|
|
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.4.3 追踪断言错误信息
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.4.3 Tracking assertion error messages
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```C
|
|
|
|
|
void cm_backtrace_assert(uint32_t sp)
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|参数 |描述|
|
|
|
|
|
|:----- |:----|
|
|
|
|
|
|sp |断言环境时的堆栈指针|
|
|
|
|
|
|Parameter |Description|
|
|
|
|
|
|:----- |:----|
|
|
|
|
|
|sp |Stack pointer when asserting environment|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
> **注意** :入参 SP 尽量在断言函数内部获取,而且尽可能靠近断言函数开始的位置。当在断言函数的子函数中(例如:在 RT-Thread 的断言钩子方法中)使用时,由于函数嵌套会存在寄存器入栈的操作,此时再获取 SP 将发生变化,就需要人为调整(加减固定的偏差值)入参值,所以作为新手 **不建议在断言的子函数** 中使用该函数。
|
|
|
|
|
> **Note**: The input parameter SP should be obtained inside the assertion function as much as possible, and as close as possible to the beginning of the assertion function. When used in the sub-function of the assertion function (for example: in the assertion hook method of RT-Thread), due to the nesting of the function, there will be the operation of registering the stack, and the SP will be changed at this time, and manual adjustment is required ( Add and subtract a fixed deviation value) into the parameter value, so as a novice, it is not recommended to use this function in the sub-function of the assertion.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.4.4 追踪故障错误信息
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.4.4 Tracking fault information
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```C
|
|
|
|
|
void cm_backtrace_fault(uint32_t fault_handler_lr, uint32_t fault_handler_sp)
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|参数 |描述|
|
|
|
|
|
|:----- |:----|
|
|
|
|
|
|fault_handler_lr |故障处理函数环境下的 LR 寄存器值|
|
|
|
|
|
|fault_handler_sp |故障处理函数环境下的 SP 寄存器值|
|
|
|
|
|
|Parameter |Description|
|
|
|
|
|
|:----- |:----|
|
|
|
|
|
|fault_handler_lr |LR register value under fault handling function environment|
|
|
|
|
|
|fault_handler_sp |SP register value under fault handling function environment|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
该函数可以在故障处理函数(例如: `HardFault_Handler`)中调用。另外,库本身提供了 `HardFault` 处理的汇编文件([点击查看](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/tree/master/cm_backtrace/fault_handler),需根据自己编译器进行选择),会在故障时自动调用 `cm_backtrace_fault` 方法。所以移植时,最简单的方式就是直接使用该汇编文件。
|
|
|
|
|
This function can be called in the fault handling function (for example: `HardFault_Handler`). In addition, the library itself provides assembly files processed by `HardFault` ([click to view](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/tree/master/cm_backtrace/fault_handler), you need to choose according to your own compiler), The `cm_backtrace_fault` method is automatically called in the event of a fault. So when transplanting, the easiest way is to use the assembly file directly.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 2.5 常见问题
|
|
|
|
|
### 2.5 FAQ
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.5.1 编译出错,提示需要 C99 支持
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.5.1 Compilation error, suggesting that C99 support is required
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[点击查看教程:一步开启 Keil/IAR/GCC 的 C99 支持](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/blob/master/docs/zh/enable_c99_for_keil_iar_gcc.md)
|
|
|
|
|
[Click to view the tutorial: Open Keil/IAR/GCC C99 support in one step](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/blob/master/docs/zh/enable_c99_for_keil_iar_gcc.md)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.5.2 如何查看到函数调用栈中函数的具体名称及代码行号
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.5.2 How to view the specific name and code line number of the function in the function call stack
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
[点击查看教程:如何使用 addr2line 工具获取函数调用栈详细信息](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/blob/master/docs/zh/how_to_use_addr2line_for_call_stack.md)
|
|
|
|
|
[Click to view the tutorial: How to use the addr2line tool to get the function call stack details](https://github.com/armink/CmBacktrace/blob/master/docs/zh/how_to_use_addr2line_for_call_stack.md)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.5.3 故障处理函数:HardFault_Handler 重复定义
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.5.3 Fault handling function: HardFault_Handler repeated definition
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
在使用了本库提供的 cmb_fault.s 汇编文件时,因为该汇编文件内部已经定义了 HardFault_Handler ,所以如果项目中还有其他地方定义了该函数,则会提示 HardFault_Handler 被重复定义的错误。此时有两种解决方法:
|
|
|
|
|
When the cmb_fault.s assembly file provided by this library is used, because HardFault_Handler is already defined in the assembly file, if this function is defined elsewhere in the project, an error that HardFault_Handler is repeatedly defined will be prompted. There are two solutions at this time:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 1、注释/删除其他文件中定义的 `HardFault_Handler` 函数,仅保留 cmb_fault.s 中的;
|
|
|
|
|
- 2、将 cmb_fault.s 移除工程,手动添加 `cm_backtrace_fault` 函数至现有的故障处理函数,但需要注意的是,务必 **保证该函数数入参的准备性** ,否则可能会导致故障诊断功能及堆栈打印功能无法正常运行。所以如果是新手,不推荐第二种解决方法。
|
|
|
|
|
1. Comment/delete the `HardFault_Handler` function defined in other files, and only keep the cmb_fault.s;
|
|
|
|
|
2. Remove cmb_fault.s from the project, and manually add the `cm_backtrace_fault` function to the existing fault handling function, but it should be noted that you must ** ensure the readiness of the function to enter the parameters**, otherwise it may cause The fault diagnosis function and stack printing function cannot operate normally. So if you are a novice, the second solution is not recommended.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.5.4 初始化时提示无法获取主栈(main stack)信息
|
|
|
|
|
#### 2.5.4 Prompt that the main stack information cannot be obtained during initialization
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
在 `cmd_def.h` 中有定义默认的主栈配置,大致如下:
|
|
|
|
|
The default main stack configuration is defined in `cmd_def.h`, roughly as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```c
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
#if defined(__CC_ARM)
|
|
|
|
|
/* C stack block name, default is STACK */
|
|
|
|
|
/* C stack block name,default is STACK */
|
|
|
|
|
#ifndef CMB_CSTACK_BLOCK_NAME
|
|
|
|
|
#define CMB_CSTACK_BLOCK_NAME STACK
|
|
|
|
|
#define CMB_CSTACK_BLOCK_NAME STACK
|
|
|
|
|
#endif
|
|
|
|
|
...
|
|
|
|
|
#elif defined(__ICCARM__)
|
|
|
|
|
/* C stack block name, default is 'CSTACK' */
|
|
|
|
|
/* C stack block name, default is'CSTACK' */
|
|
|
|
|
#ifndef CMB_CSTACK_BLOCK_NAME
|
|
|
|
|
#define CMB_CSTACK_BLOCK_NAME "CSTACK"
|
|
|
|
|
#define CMB_CSTACK_BLOCK_NAME "CSTACK"
|
|
|
|
|
#endif
|
|
|
|
|
...
|
|
|
|
|
#elif defined(__GNUC__)
|
|
|
|
|
/* C stack block start address, defined on linker script file, default is _sstack */
|
|
|
|
|
#ifndef CMB_CSTACK_BLOCK_START
|
|
|
|
|
#define CMB_CSTACK_BLOCK_START _sstack
|
|
|
|
|
#define CMB_CSTACK_BLOCK_START _sstack
|
|
|
|
|
#endif
|
|
|
|
|
/* C stack block end address, defined on linker script file, default is _estack */
|
|
|
|
|
#ifndef CMB_CSTACK_BLOCK_END
|
|
|
|
|
#define CMB_CSTACK_BLOCK_END _estack
|
|
|
|
|
#define CMB_CSTACK_BLOCK_END _estack
|
|
|
|
|
#endif
|
|
|
|
|
...
|
|
|
|
|
#else
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
比如在 Keil-MDK 编译器下会默认选择 `STACK` 作为主栈 block 的名称,但在一些特殊平台下,项目的主栈 block 名称可能不叫 `STACK`,导致 CmBacktrace 无法获取到正确的主栈信息,所以在初始化时会有如上的错误提示信息。
|
|
|
|
|
For example, under the Keil-MDK compiler, `STACK` will be selected as the name of the main stack block by default, but under some special platforms, the name of the main stack block of the project may not be called `STACK`, causing CmBacktrace to fail to obtain the correct main stack Information, so there will be the above error message during initialization.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
解决这个问题一般有两个思路
|
|
|
|
|
There are generally two ways to solve this problem
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 1、在 `cmb_cfg.h` 中重新定义主栈的信息,此时 CmBacktrace 会优先使用 `cmb_cfg.h` 中的配置信息;
|
|
|
|
|
- 2、修改项目配置,如果是 Keil-MDK ,则在启动文件的开头位置,将主栈的名称修改为默认的 `STACK` ,其他编译器一般很少出现该问题。
|
|
|
|
|
1. Redefine the main stack information in `cmb_cfg.h`. At this time, CmBacktrace will give priority to using the configuration information in `cmb_cfg.h`;
|
|
|
|
|
2. Modify the project configuration. If it is Keil-MDK, change the name of the main stack to the default `STACK` at the beginning of the startup file. This problem rarely occurs with other compilers.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 2.6 许可
|
|
|
|
|
### 2.6 License
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
采用 MIT 开源协议,细节请阅读项目中的 LICENSE 文件内容。
|
|
|
|
|
The MIT open source agreement is adopted. For details, please read the contents of the LICENSE file in the project.
|